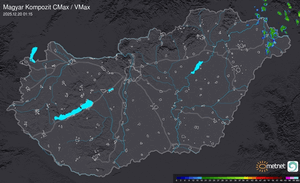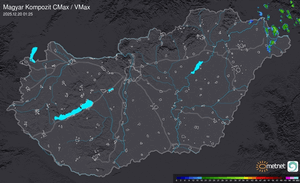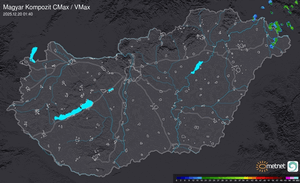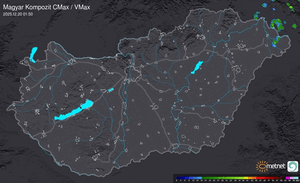
Külföldi időjárási események
blizzard—A severe weather condition characterized by high winds and reduced visibilities due to falling or blowing snow.
The U.S. National Weather Service specifies a wind of 30 knots (35 miles per hour) or greater, sufficient snow in the air to reduce visibility to less than 400 m (0.25 miles). Earlier definitions also included a condition of low temperatures, on the order of −7°C (20°F) or lower, or −12°C (10°F) or lower (severe blizzard). The name originated in the United States but it is also used in other countries. In the Antarctic the name is given to violent autumnal winds off the ice cap. In southeastern France, the cold north wind with snow is termed blizzard (see also boulbie). Similar storms in Russian Asia are the buran and purga. In popular usage in the United States and in England, the term is often used for any heavy snowstorm accompanied by strong winds.
Link
According to Environment Canada, a winter storm must have winds of 40 km/h (25 mph) or more, have snow or blowing snow, visibility less than 1 km (about 5⁄8 mile), a wind chill of less than −25 °C (−13 °F), and that all of these conditions must last for 4 hours or more before the storm can be properly called a blizzard.
In the United States, the National Weather Service defines a blizzard as sustained 35 mph (56 km/h) winds which lead to blowing snow and cause visibilities of ¼ mile or less, lasting for at least 3 hours. Temperature is not taken into consideration when issuing a blizzard warning, but the nature of these storms is such that cold air is often present when the other criteria are met.[1] . Temperatures are generally below 0 degrees F.
Other countries, such as the UK, have a lower threshold: the Met Office defines a blizzard as "moderate or heavy snow" combined with a mean wind speed of 30 mph (48 km/h) and visibility below 650 feet (200 m).
Link
The U.S. National Weather Service specifies a wind of 30 knots (35 miles per hour) or greater, sufficient snow in the air to reduce visibility to less than 400 m (0.25 miles). Earlier definitions also included a condition of low temperatures, on the order of −7°C (20°F) or lower, or −12°C (10°F) or lower (severe blizzard). The name originated in the United States but it is also used in other countries. In the Antarctic the name is given to violent autumnal winds off the ice cap. In southeastern France, the cold north wind with snow is termed blizzard (see also boulbie). Similar storms in Russian Asia are the buran and purga. In popular usage in the United States and in England, the term is often used for any heavy snowstorm accompanied by strong winds.
Link
According to Environment Canada, a winter storm must have winds of 40 km/h (25 mph) or more, have snow or blowing snow, visibility less than 1 km (about 5⁄8 mile), a wind chill of less than −25 °C (−13 °F), and that all of these conditions must last for 4 hours or more before the storm can be properly called a blizzard.
In the United States, the National Weather Service defines a blizzard as sustained 35 mph (56 km/h) winds which lead to blowing snow and cause visibilities of ¼ mile or less, lasting for at least 3 hours. Temperature is not taken into consideration when issuing a blizzard warning, but the nature of these storms is such that cold air is often present when the other criteria are met.[1] . Temperatures are generally below 0 degrees F.
Other countries, such as the UK, have a lower threshold: the Met Office defines a blizzard as "moderate or heavy snow" combined with a mean wind speed of 30 mph (48 km/h) and visibility below 650 feet (200 m).
Link